Facebook claims $50,000 in revenue. Google says $35,000. Email shows $22,000. Total attributed: $107,000. Your client’s actual revenue: $68,000.
Your client sees this math every month. They know it doesn’t add up. This is why media-only agencies have an average client relationship of just 44 months (3.7 years), while integrated full-service agencies that provide strategic business insights average 87 months (7.3 years) according to ANA research.
The problem isn’t your campaigns. It’s that you’re tracking marketing metrics while your clients need business metrics. When they ask about cash flow impact and you show them click-through rates, you become expendable.
This guide shows you the five metrics that actually predict ecommerce success and how to present them in ways that make you indispensable to your client’s growth.
Essential Ecommerce Metrics That Drive Real Business Success
Why It’s Important: The master metric that determines whether your business model is sustainable and profitable.
What Does It Measure: Business health and long-term viability by comparing customer value to acquisition cost.
Benchmark: Healthy ecommerce businesses should have a ratio of at least 3:1, with top performers achieving 5:1 or higher.
Best For: Determining budget allocation and business sustainability.
Related Metrics: Customer Payback Period, True CAC.
Common Pitfalls: Using overall averages instead of monthly cohorts, missing the improvement trends in recent acquisitions.
Pro tip: Use GA4’s User Lifetime Value report for predictive CLV with machine learning, combine with CAC data from your ad platforms.
Why It’s Important: Shows when marketing investments start generating positive returns and impacts cash flow planning.
What Does It Measure: How quickly customers become profitable after acquisition.
Benchmark: Ideally under 90 days; 30-60 days is excellent for most ecommerce businesses.
Best For: Cash flow planning and growth sustainability assessment.
Related Metrics: CLV:CAC Ratio, Monthly Recurring Revenue.
Common Pitfalls: Not accounting for seasonal variations or different payback periods by channel.
Pro tip: Calculate using AOV and frequency data from Shopify, combine with CAC from your ad platforms (Google Ads, Facebook Ads Manager).
Why It’s Important: Reveals the real cost of acquiring customers by including all hidden expenses, not just ad spend.
What Does It Measure: Complete cost structure of customer acquisition including creative, tools, and team costs.
Benchmark: Often 30-70% higher than reported CAC when all costs are included.
Best For: Accurate profitability analysis and budget planning.
Related Metrics: CLV:CAC Ratio, ROAS.
Common Pitfalls: Only tracking ad spend and missing substantial operational costs that impact true profitability.
Pro tip: Create a monthly expense tracker that includes all hidden costs – creative production, tools, team allocation, platform fees. Most accurate when done manually.
Why It’s Important: Identifies which marketing channels bring customers who actually stick around and buy again.
What Does It Measure: Customer quality and loyalty by acquisition source.
Benchmark: Varies by industry; 20-40% is typical for most ecommerce categories.
Best For: Channel quality assessment and budget allocation decisions.
Related Metrics: Customer Lifetime Value, Average Order Value.
Common Pitfalls: Optimizing for acquisition volume without considering customer quality and retention.
Pro tip: Use Shopify’s Customer Cohort Analysis report to track repeat purchase rates by acquisition channel with built-in attribution.
Why It’s Important: Optimizes cash flow by showing which products move fast and which tie up capital.
What Does It Measure: How quickly inventory converts to sales and generates cash flow.
Benchmark: 6-12 times per year for most ecommerce businesses, varies significantly by category.
Best For: Ad spend allocation and inventory management optimization.
Related Metrics: Inventory Velocity Score, Stockout Risk.
Common Pitfalls: Promoting slow-moving inventory without considering opportunity cost of faster-moving products.
Pro tip: Connect inventory management system APIs to your ad platforms for automated bid adjustments based on stock levels.
Why It’s Important: Reveals hidden patterns in customer spending and identifies upselling opportunities.
What Does It Measure: Spending patterns across different customer segments and channels.
Benchmark: Highly industry-dependent; focus on trends and segment comparisons rather than absolute values.
Best For: Understanding customer behavior and optimizing product recommendations.
Related Metrics: Purchase Frequency, Customer Lifetime Value.
Common Pitfalls: Assuming higher AOV always means better customers without considering purchase frequency.
Pro tip: Use GA4’s custom segments to track AOV by device, channel, and customer type. Shopify’s native reports show AOV trends over time.
Why It’s Important: Prevents revenue loss by identifying at-risk customers 30-60 days before they actually churn.
What Does It Measure: Behavioral indicators that predict customer departure.
Benchmark: 78% prediction accuracy is achievable with proper behavioral tracking.
Best For: Proactive retention campaigns and revenue protection.
Related Metrics: Customer Lifetime Value, Repeat Purchase Rate.
Common Pitfalls: Waiting for customers to actually churn before implementing retention efforts.
Pro tip: GA4’s machine learning predicts purchase probability and retention. Klaviyo identifies at-risk customers based on email engagement patterns.
Why It’s Important: Predicts CAC increases and identifies market opportunities before competitors react.
What Does It Measure: Your percentage of total search impressions and social conversations in your category.
Benchmark: Varies by market maturity; 15-25% is strong for most competitive categories.
Best For: Strategic planning and competitive positioning.
Related Metrics: Market Share Movement, Competitive Pressure Index.
Common Pitfalls: Focusing only on your own performance without understanding market context.
Pro tip: Use Semrush’s Market Explorer for search share of voice and Facebook Ad Library for social advertising visibility tracking.
Why It’s Important: Exposes targeting problems and reveals true customer satisfaction by acquisition source.
What Does It Measure: Product-market fit and customer expectation alignment across different channels.
Benchmark: 10-30% depending on category; significant variations between channels indicate targeting issues.
Best For: Channel optimization and customer quality assessment.
Related Metrics: Net Promoter Score, Customer Satisfaction.
Common Pitfalls: Treating high return rates as product issues when they’re actually targeting misalignment.
Pro tip: Set up return tracking in GA4 with custom dimensions for acquisition channel. Shopify’s native return reports show patterns by product.
Why It’s Important: Shows what revenue would actually disappear if campaigns stopped, beyond inflated attribution reports.
What Does It Measure: True marketing impact versus revenue that would have happened anyway.
Benchmark: 30-50% of attributed revenue typically would have happened anyway; focus on incremental lift.
Best For: Accurate budget allocation and performance measurement.
Related Metrics: True ROAS, Cross-Channel Attribution.
Common Pitfalls: Relying solely on last-click attribution when customer journeys span multiple touchpoints and timeframes.
Pro tip: Run geo-holdout tests using Facebook’s Conversion Lift or Google’s geographical experiments. GA4’s data-driven attribution shows cross-channel impact.
Why Good Marketing Campaigns Can Destroy Profitable Businesses
Take this scenario. You’re running campaigns for a mid-sized outdoor gear company. Your dashboard looks incredible. 4.8x ROAS. 23% decrease in cost-per-acquisition. 156% increase in conversion volume. You’re feeling pretty good about yourself.
Six months later, your client is in crisis mode. Despite your “successful” campaigns, they’re hemorrhaging cash. Customer retention has collapsed. The founder is considering shutting down operations. What happened?
Your low-CAC strategy attracted bargain hunters who bought once on deep discounts and never returned. You optimized for acquisition volume while accidentally destroying customer lifetime value. The business model you helped create was fundamentally unsustainable.
Think about it. When was the last time you actually calculated whether the customers you’re acquiring will be profitable long-term? Or whether your campaigns are improving or destroying their unit economics?
This happens because ecommerce businesses operate with complex constraints that most agency owners never learn about. Your client pays for inventory 90-120 days before selling it. They pay for your advertising 30 days before seeing results. Then they wait 15-30 days for payment processing. That 40% revenue increase you delivered might actually create a cash flow crisis if those customers have high return rates or low repeat purchase rates.
Another reality check comes when you examine inventory dynamics. Your “successful” campaign driving 300% more sales of blue widgets means nothing if they only have 50 blue widgets in stock and can’t reorder for six weeks. Meanwhile, you’re burning their budget on out-of-stock products while neglecting available inventory.
The uncomfortable truth? You can literally optimize an ecommerce business into bankruptcy when you focus on the wrong metrics.
How Attribution Reports Destroy Client Trust and What to Do About It
Let’s address the elephant in the room. Your attribution reports don’t match your client’s reality.
Facebook claims your campaigns drove $50,000 in revenue last month. Google says their campaigns drove $35,000. Your email platform reports $22,000. Add it up and you’ve “driven” $107,000 in revenue from a business that only generated $68,000 total.
| Platform | Claimed Revenue |
|---|---|
| $50,000 | |
| $35,000 | |
| $22,000 | |
| Total Attributed | $107,000 |
| Actual Revenue | $68,000 |
| Attribution Gap | $39,000 (57% inflated) |
Your client sees this discrepancy every month. They’re not stupid. They know the math doesn’t work. This creates a fundamental trust problem where they start questioning everything you tell them.
When your reported results don’t match their bank account, you look either incompetent or dishonest. Neither is a good position for maintaining long-term client relationships.
Have you wondered why your most successful campaigns on paper sometimes coincide with your clients expressing concerns about cash flow? The solution isn’t better attribution. It’s understanding what revenue would actually disappear if your campaigns stopped running.
This requires incrementality testing. Testing typically reveals that a significant portion of attributed revenue would have happened anyway through other channels, as digital attribution typically claims credit for all sales following any touchpoint. But here’s what’s interesting. Incrementality testing also often reveals hidden value that attribution systems completely miss. You might find that your display campaigns drive 40% of organic search volume. Or that your Facebook campaigns influence 60% of email conversions.
The Cash Flow Framework That Transforms Agency Client Conversations
Most agencies think ecommerce is straightforward. Drive traffic, optimize for conversions, celebrate revenue growth. But successful ecommerce businesses are actually sophisticated financial instruments with dozens of interconnected variables.
Each ecommerce business is essentially a cash flow equation. When you understand this equation, you stop optimizing for vanity metrics and start optimizing for business outcomes.
| Marketing Metrics (What You Track) | Business Metrics (What Clients Need) | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| ROAS: 4.2x | Customer Payback Period: 67 days | Shows cash flow impact |
| CAC: $47 | True CAC: $80 (including hidden costs) | Reveals real profitability |
| Conversion Rate: 3.2% | Inventory Velocity: 45 days | Aligns spend with stock |
| CTR: 2.4% | CLV:CAC Ratio: 4.9:1 | Predicts sustainability |
| Email Open Rate: 23% | Churn Warning Signals: 60 days out | Enables prevention |
Instead of saying “Our Facebook campaigns generated $47,000 in revenue with a 4.2x ROAS,” you say “Our Facebook optimizations reduced your customer payback period from 89 days to 67 days, which frees up $31,000 in working capital that you can reinvest in inventory for holiday season.”
This shift in language immediately positions you as someone who understands their business, not just their marketing.
The Complete Metrics Arsenal That Drives Real Business Success
Let me walk you through the metrics that transform agency-client relationships. I’ve organized these into strategic tiers based on business impact.
Business Foundation Metrics That Determine Survival
These metrics determine whether your client’s business model is fundamentally sound and sustainable. Get these wrong, and no amount of marketing optimization will save them.
Customer Lifetime Value to Customer Acquisition Cost Ratio Shows Business Health
This is the master metric that determines whether your client’s business model is sustainable. Think of it as the heartbeat of their business. A healthy ecommerce business should have a CLV:CAC ratio of at least 3:1, with the best performers achieving 5:1 or higher.
Most agencies get it wrong when they calculate this as an overall average. But you should calculate it using monthly acquisition cohorts. You might find that customers you acquired last month have a 4.9:1 ratio while your overall historical average is 2.8:1. This insight allows you to increase spend aggressively because recent performance is much stronger than historical data suggests.
Let’s say you’re managing campaigns for a skincare brand. Your overall CLV:CAC ratio looks mediocre at 2.3:1. But when you dig into cohorts, you find that customers acquired through your optimized Google campaigns in March are tracking a 4.9:1 ratio. This completely changes the conversation with your client.
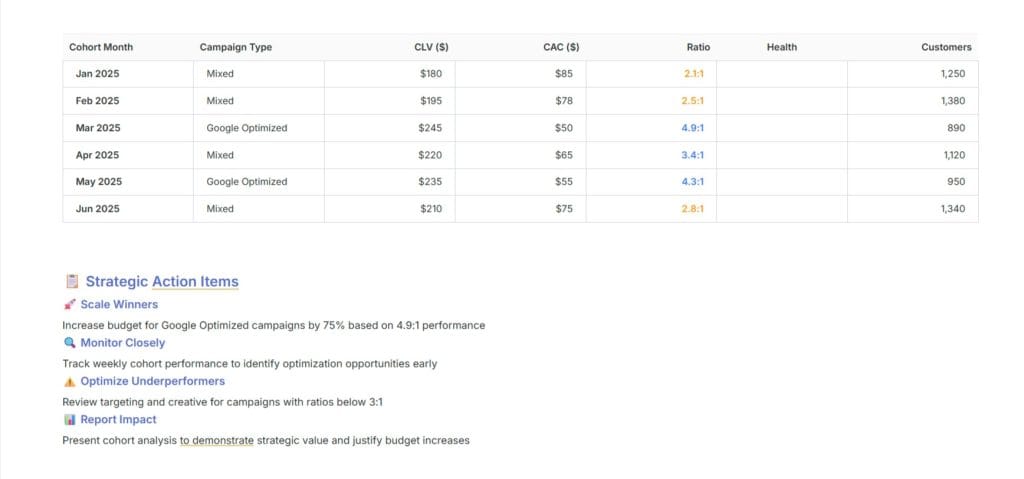
Your strategic conversation becomes: “Your March acquisition cohort is tracking a 4.9:1 CLV:CAC ratio, compared to your historical average of 2.8:1. This improvement suggests our targeting optimizations are working. Based on this performance, we can increase spend roughly 75% while maintaining your profitability thresholds.”
Can you see how this positions you as a strategic advisor rather than a campaign manager?
CLV:CAC Ratio Calculator
Calculate your Customer Lifetime Value to Customer Acquisition Cost ratio
Performance Benchmarks
Average Order Value Analysis Reveals Hidden Opportunities
AOV reveals spending patterns and helps identify upselling opportunities. But the real insight comes from segmentation. Track AOV across acquisition channel, customer lifetime stage, and device type. You might find that mobile customers have 40% lower AOV but 60% higher purchase frequency, making them more valuable long-term despite appearing less attractive initially.
Take a real scenario you might encounter. Your Google campaigns generate $89 AOV while Facebook delivers $156 AOV. On the surface, Facebook looks better. But when you analyze repeat purchase behavior, Google customers place 3x more orders annually. This means Google's apparent lower efficiency actually generates 140% higher lifetime value per customer.
Your client conversation shifts from defending low AOV to explaining superior customer quality: "While Facebook customers spend 75% more per order, Google customers place 3.2x more orders annually. This means Google's apparent lower efficiency actually generates 140% higher lifetime value per customer."
True Customer Acquisition Cost Includes All Hidden Expenses
Most agencies calculate CAC using only paid media spend, missing 30-50% of actual acquisition costs.
Include creative production, landing page development, attribution software, team salaries allocated to acquisition, and platform fees. This gives you the real cost of customer acquisition that determines business sustainability.
| Cost Component | $ Per Customer | Often Missed? |
|---|---|---|
| Ad Spend | $47 | No |
| Creative Production | $12 | Yes |
| Platform Management Fees | $8 | Yes |
| Attribution Software | $3 | Yes |
| Landing Page Development | $5 | Yes |
| Team Salaries (allocated) | $5 | Yes |
| True CAC | $80 | |
| Reported CAC | $47 | |
| Hidden Costs | $33 (70% higher) |
Your Facebook CAC might appear to be $47. But when you include creative production costs ($12 per customer), platform management fees ($8 per customer), and attribution software ($3 per customer), the true CAC is $80. This 70% difference completely changes budget allocation decisions.
Customer Experience Metrics That Predict Long Term Success
These metrics reveal how well your acquisition strategies align with long-term business success.
Sales Conversion Rate Analysis By Traffic Source and Device
Basic conversion rate tells you nothing. Sophisticated conversion rate analysis reveals optimization opportunities. Track conversion rates across traffic source, device type, time of day, and customer type.
You might find that mobile traffic converts at 1.2% overall but returning mobile customers convert at 8.4%. This insight suggests mobile optimization should focus on retention rather than acquisition. If your Facebook mobile traffic converts at 0.9% while desktop converts at 3.7%, but mobile users have 2.3x higher lifetime value, you need mobile-specific optimization rather than budget reduction.
Shopping Cart Abandonment Patterns Show Revenue Recovery Potential
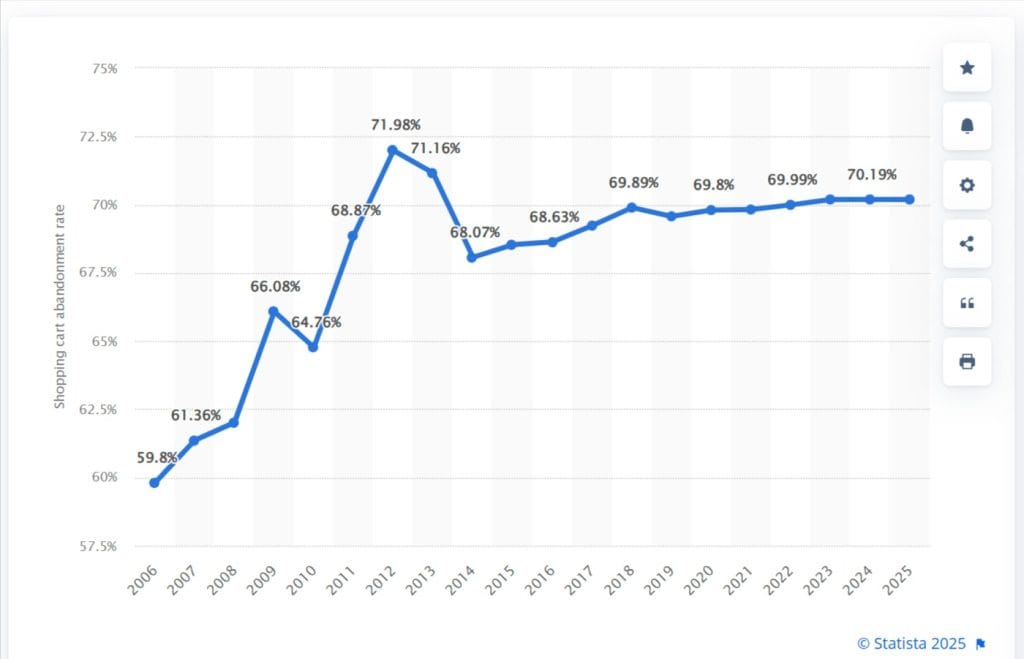
According to Statista, almost 70% of shoppers abandon their carts. Lots of factors impact such a drastic number:
- Unexpected shipping expenses;
- Complex checkout process;
- Forcing customers to create an account;
- Long delivery;
- Unclear return and refund policy;
- Limited payment options;
- Security concerns.
Cart abandonment reveals intent gaps, but recovery analysis shows optimization potential. Track abandonment at each stage and implement stage-specific recovery strategies.
You might find that 34% of cart abandoners complete purchases within 72 hours through email recovery campaigns. Another 23% return within 7 days organically. Only 43% are truly lost. This changes how you calculate the real impact of cart abandonment.
Your optimization strategy becomes specific: "Cart abandonment at the payment stage represents 67% of total abandonment, suggesting payment friction rather than price sensitivity. Adding PayPal and Apple Pay could recover an estimated $34,000 monthly in lost revenue."
Customer Retention Patterns Reveal Marketing Quality
Retention metrics predict business sustainability and reveal marketing quality. Track retention across acquisition cohort and channel. Customers acquired through different campaigns might have dramatically different retention patterns.
The sophisticated approach involves predictive modeling. Identify early churn signals like declining email engagement, increased time between purchases, or customer service interactions. This allows you to implement prevention campaigns 30-60 days before customers actually churn.
Net Promoter Score Differences Predict Organic Growth
NPS predicts organic growth potential and reveals customer quality differences. But most agencies miss the key insight. Track NPS across acquisition channel, customer lifetime value, and purchase recency. High-value customers' NPS scores predict future growth better than overall NPS.
If customers acquired through your Google campaigns have an NPS of 67 while Facebook-acquired customers score 23, this predicts significantly different referral rates and organic growth potential.
Operational Performance Metrics That Impact Profitability
These metrics reveal operational efficiency and inventory management effectiveness.
Return Rate Variations Expose Targeting Problems
Return rates reveal product-market fit and customer expectation alignment. Track return rates across acquisition channel. If Facebook customers have 43% return rates while Google customers have 12% rates, this suggests targeting misalignment rather than product issues.
Return rates often vary across season, customer type, and product category. Holiday shoppers might have 67% higher return rates but still be profitable due to higher AOV and gift card usage.
Inventory Velocity Guides Smart Ad Spend Allocation
This metric reveals demand patterns and helps optimize ad spend allocation. Align ad spend with inventory velocity. Promoting products with 4-day inventory remaining while neglecting 90-day inventory creates lost revenue opportunities.
Use velocity trends to predict stockouts 2-4 weeks in advance, allowing budget reallocation to available inventory before competitors capture demand.
Marketing Performance Metrics That Show True Impact
These metrics measure marketing efficiency and cross-channel effectiveness.
Website Traffic Quality Beats Traffic Volume Every Time
Traffic volume means nothing without quality analysis. Track bounce rate by source, store sessions by device type, sessions by location, and returning customer rate.
If mobile represents 73% of traffic but only 34% of revenue, you need mobile-specific optimization rather than mobile budget reduction. The goal isn't to reduce mobile traffic but to improve mobile conversion.
Email Marketing ROI Measured By Revenue Not Opens
Email metrics without business impact are vanity metrics. Track open rates by customer segment, send time, and subject line type. B2B customers might open emails 340% more often on weekdays, while B2C customers prefer weekend sends.
Connect email engagement to actual revenue. An email with 12% click-through rate that generates $47 per recipient is more valuable than one with 23% CTR generating $12 per recipient.
Social Media Impact Goes Beyond Platform Metrics
Social metrics need business context to drive decisions. Track reach versus revenue correlation, engagement by customer type, and social commerce conversion rates.
Track customers who engage socially before purchasing through other channels. Social engagement might drive 40% of email sign-ups and 60% of organic search volume.
Cross Channel Attribution Windows Reveal Hidden Value
Standard last-click attribution misses 40-70% of marketing's actual influence. Understand attribution at multiple time horizons:
| Attribution Window | Purpose | Weight | What It Captures |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-day | Immediate response | 20% | Impulse purchases, direct response |
| 7-day | Consideration period | 40% | Research phase, comparison shopping |
| 28-day | Full journey | 30% | Complex decisions, B2B cycles |
| 90-day view | Brand building | 10% | Long-term impact, word-of-mouth |
Map customer touchpoints across all channels to understand optimal sequences. Display campaigns followed by search then email typically generates 34% higher lifetime value than single-channel acquisitions.
You'll often find that campaigns appearing marginally profitable in last-click attribution are actually driving 40-60% of downstream conversions from other channels.

Advanced Competitive Intelligence Predicts Market Changes Before They Happen
Most agencies operate in isolation, optimizing campaigns without understanding market dynamics. Competitive intelligence provides context that transforms good campaigns into market-dominating strategies.
Monitor how quickly you're gaining or losing market share relative to competitors. Track your percentage of total search impressions in your category, your percentage of social conversations, keywords where competitors rank but you don't, and direct competition frequency with specific competitors.
Rising competitive pressure typically predicts 15-30% higher CACs within 60-90 days. This allows proactive budget adjustments rather than reactive crisis management. Declining competitive pressure indicates opportunity for market share expansion.
You might identify that your main competitor reduced search spend 40% due to inventory constraints, creating a 4-6 week window to capture additional market share.
Use historical data to predict future customer actions. Declining purchase frequency, reduced email engagement, increased time between purchases, changes in product preferences, and customer service interaction patterns all signal potential churn.
Preventing customer churn is 5-10x more cost-effective than acquiring new customers. You can identify at-risk customers 30-60 days before they churn and implement retention campaigns.
Technology Infrastructure That Creates Competitive Advantages
The right technology doesn't just improve efficiency. It creates capabilities that competitors can't easily replicate.
Server Side Tracking Captures 30% More Conversion Data
Client-side tracking through pixels and cookies is increasingly unreliable due to iOS updates and privacy regulations. Server-side tracking captures 15-30% more conversion data while respecting privacy requirements. This requires:
- Google Tag Manager Server-Side Container
- Facebook Conversions API
- Enhanced Ecommerce tracking
- Custom event tracking
Incrementality Testing Reveals True Campaign Impact
Use geographic regions to compare performance in test markets with campaigns versus control markets without campaigns. This requires:
- Minimum 20 geographic regions for statistical significance
- 4-8 week testing periods
- Statistical significance testing
Incrementality testing typically reveals that 30-50% of attributed conversions would have happened anyway, but also uncovers hidden value that attribution systems miss. Net result is usually 20-40% improvement in budget allocation efficiency.
Transform Client Relationships Through Strategic Business Reviews
When you get a handle on these metrics, your client relationships fundamentally change. Transform your standard performance reviews into strategic business planning sessions.
Quarterly Business Reviews Become Strategic Planning Sessions
Structure your quarterly business reviews differently:
Business Health Assessment (20 minutes)
- CLV:CAC trend analysis
- Cash flow impact of marketing activities
- Customer quality shifts across channels
- Competitive position changes
Market Intelligence Briefing (15 minutes)
- Competitive threat analysis
- Emerging market opportunities
- Seasonal demand predictions
- Category expansion possibilities
Strategic Recommendations (15 minutes)
- Budget allocation optimization
- New channel opportunities
- Testing roadmap for next quarter
- Long-term growth strategy alignment
Instead of defending past performance, you're guiding future strategy. Your clients start viewing you as a business consultant who executes marketing campaigns, not a marketing vendor who provides reports.
Annual Planning Partnerships Drive Long Term Retention
Position yourself as essential to your client's strategic planning process. Develop growth scenario modeling with conservative, aggressive, and breakthrough growth scenarios. Include budget requirements for each scenario, expected outcomes and risk factors, and ROI projections by channel and timeframe.
Create market opportunity assessments covering:
- Total addressable market analysis
- Competitive landscape mapping
- Customer acquisition potential by channel
- Category expansion opportunities
Your value proposition becomes: "Based on our analysis, increasing your marketing budget 60% next year would improve your CLV:CAC ratio to 5.2:1 while reducing customer payback period to 52 days. This creates a self-funding growth engine that could scale to $2.8M annual revenue without additional capital requirements."
Cash Flow Prediction Metrics Help Clients Plan Growth
Help your clients understand when money will come in and go out, essential for growth planning.
Customer Acquisition Cost Recovery Timeline Shows Break Even Points
Shows when marketing investments start generating positive returns.
What your client needs to know: "Email remarketing customers become profitable in 23 days while Facebook prospecting takes 78 days. We can use email profits to fund longer-term Facebook acquisition."
Seasonal Revenue Pattern Analysis Prevents Cash Crunches
Identify revenue fluctuations throughout the year to help with inventory planning and cash flow management.
What your client needs to know: "Your revenue typically drops 35% in February but jumps 180% in November. Plan inventory purchases in September to avoid stockouts during peak season."
Competitive Intelligence Metrics Identify Market Opportunities
Show your clients how they're performing relative to market conditions and competitors.
Market Share Movement Tracks Competitive Position
Track whether your client is gaining or losing ground in their market.
What your client needs to know: "Your search share of voice increased from 12% to 19% while your main competitor dropped from 31% to 24%. This represents approximately $180K in market share capture."
Competitive Pressure Index Predicts Cost Increases
Predict when acquisition costs will increase due to competitive activity.
What your client needs to know: "Competitive pressure is declining 15% this month due to competitor budget reductions. We have a 4-6 week window to capture additional market share at lower costs."
Customer Behavior Insights Drive Better Decisions
Help your clients understand how customers interact with their business and products.
Purchase Journey Analysis Optimizes Attribution Models
Track how long customers take from first visit to purchase, critical for attribution and budget allocation.
What your client needs to know: "B2B customers average 14 days from first visit to purchase with 6 touchpoints, while B2C customers average 3 days with 2 touchpoints. This affects how we structure remarketing campaigns."
Product Performance Rankings Focus on Profit Not Sales
Show which products drive the most profit, not just the most sales.
What your client needs to know: "Widget A has highest sales volume but Widget B generates 40% more profit per unit. Shifting promotion focus to Widget B could increase overall profitability by 23%."
Risk Management Metrics Prevent Business Disasters
Help your clients identify potential problems before they become critical issues.
Customer Churn Early Warning System Saves Revenue
Identify customers likely to stop buying before they actually do.
What your client needs to know: "Customers showing these behavior patterns have 78% probability of churning within 60 days. Implementing retention campaigns now could save approximately $45K in lifetime value."
Stockout Risk Predictions Prevent Lost Sales
Forecast inventory shortages before they happen.
What your client needs to know: "Based on current sales velocity, you'll run out of your best-selling product in 18 days. Reorder now to avoid losing $23K in potential sales."
Essential Business Metrics Your Clients Need to Track
Your clients aren't interested in marketing theory. They need actionable insights that directly impact their business decisions. Focus on these critical metrics that translate marketing performance into business outcomes.
Revenue Impact Metrics Show Real Business Growth
These metrics show your clients how marketing activities affect their bottom line and cash flow.
Monthly Recurring Revenue Growth Rate Indicates Momentum
Track month-over-month revenue growth to identify trends and seasonal patterns. Your client needs to understand whether growth is accelerating, plateauing, or declining.
What your client needs to know: "Your revenue growth rate has increased from 8% to 14% month-over-month since we optimized targeting. This trajectory puts you on track to hit $2.1M annual revenue."
Customer Payback Period Determines Cash Flow Health
This shows how quickly customers become profitable after acquisition. Critical for cash flow planning and growth sustainability.
What your client needs to know: "We've reduced your customer payback period from 89 to 67 days, which frees up $31,000 in working capital you can reinvest in inventory for holiday season."
Customer Quality Metrics Reveal True Value
Help your clients understand not just how many customers they're getting, but what kind of customers.
Repeat Purchase Rate by Acquisition Channel Exposes Channel Quality
Shows which marketing channels bring customers who actually stick around and buy again.
What your client needs to know: "Google customers have a 67% repeat purchase rate compared to 23% for Facebook customers. This suggests we should shift more budget to Google for long-term profitability."
Average Order Value Trends Uncover Growth Opportunities
Track AOV changes over time and by customer segment to identify upselling opportunities and customer behavior shifts.
What your client needs to know: "Mobile customers have 40% lower AOV but 60% higher purchase frequency, making them actually more valuable long-term than desktop customers."
Operational Efficiency Metrics Improve Profit Margins
These metrics help your clients optimize their business operations and inventory management.
Inventory Turnover Rate Optimizes Cash Flow
Shows which products are moving fast and which are sitting stagnant, critical for cash flow and storage costs.
What your client needs to know: "Your outdoor gear is turning over every 45 days while accessories take 120 days. We should shift ad spend toward faster-moving categories to improve cash flow."
Return Rate Analysis Identifies Quality Issues
Track return rates by product, channel, and customer type to identify quality issues or targeting problems.
What your client needs to know: "Facebook customers have 43% return rates while Google customers have 12% rates. This suggests Facebook targeting is attracting customers with different expectations."
Essential Tools for Business Metrics Tracking
Different metrics require different tools. Here's what you need to actually measure what matters to your clients.
Attribution and Revenue Tracking Platforms
Triple Whale or Northbeam Best for unified ecommerce attribution across all channels. Shows true customer journeys and revenue attribution.
Google Analytics 4 with Enhanced Ecommerce Free option that tracks basic conversion funnels and customer behavior. Configure properly for accurate revenue reporting.
Shopify/WooCommerce Built-in Analytics Platform-specific data that's often more accurate than third-party tools for core metrics like AOV and repeat purchase rates.
Customer Quality Analysis Software
Klaviyo Excellent for tracking customer lifetime value, segmentation, and email performance by acquisition channel.
Gorgias + Customer Service Data Track support ticket volume and resolution time by customer acquisition source to understand true customer quality.
Competitive Intelligence Tools
Semrush or Ahrefs Monitor competitor search spend, keyword rankings, and market share changes.
Facebook Ad Library + Manual Monitoring Track competitor creative strategies and spend fluctuations.
Inventory and Operations Systems
Inventory Management System APIs Connect directly to your client's inventory system for real-time stock levels and velocity data.
Custom Dashboards (Swydo) Combine data from multiple sources into client-friendly reporting dashboards.
Common Pitfalls That Destroy Metrics Programs
Don't try to implement every metric simultaneously. Start with the core four and expand gradually. Choose 5-7 metrics maximum for your first 90 days. Get complete control of those before adding complexity.
Data Quality Issues Undermine Credibility
Your clients don't want more data. They want clearer insights that drive decisions. Each metric you present must answer a specific business question and suggest a clear action.
Wait for statistically significant sample sizes before making major recommendations. Establish minimum sample sizes and confidence intervals before drawing conclusions from metric changes.
Platform Myopia Misses The Big Picture
Don't optimize for individual platform metrics at the expense of overall business performance. Always present platform performance in the context of total business impact.
Set and Forget Mentality Leads to Obsolete Insights
Schedule monthly metric reviews and quarterly framework assessments. Metrics and benchmarks change as businesses grow and change.
Ecommerce Unit Economics Fundamentals Every Agency Must Understand
Before diving deeper into metrics, it's crucial to understand how ecommerce unit economics work. Every transaction in an ecommerce business follows this fundamental equation:
Unit Economics = (Average Order Value × Gross Margin) - (Customer Acquisition Cost + Fulfillment Cost + Processing Fees)
When this equation is positive, you have a sustainable business model. When it's negative, you're literally paying to lose money on every order. Many agencies accidentally push their clients into negative unit economics by focusing solely on top-line revenue growth without considering the full cost structure.
Key Takeaways
The ultimate goal isn't just tracking better metrics—it's becoming irreplaceable to your clients' success. Build a metrics moat by.
Stop trying to track everything. Start with these five metrics that directly impact your client's bank account:
- Customer Lifetime Value to Customer Acquisition Cost Ratio - Shows if the business model is sustainable
- Customer Payback Period - Reveals cash flow impact of marketing spend
- Repeat Purchase Rate by Channel - Identifies which marketing channels bring quality customers
- Inventory Turnover Rate - Helps optimize ad spend allocation and cash flow
- Competitive Share of Voice - Predicts CAC increases and market opportunities
Track these monthly. Present insights quarterly. Act on problems immediately.
When you own the metrics narrative, you own the client relationship. Make yourself the source of truth for business performance, not just campaign performance.
