You launch a Facebook campaign at 9 AM. By lunch, your email blast goes out. That afternoon, your Google Ads are live. Three days later, you’re staring at a spike in sales wondering which campaign actually worked. Without proper tracking, you’re essentially flying blind with your marketing budget.
This is where UTM parameters become your marketing GPS. These simple URL additions transform guesswork into certainty, showing you exactly which campaigns drive real results for your clients.
What UTM Parameters Actually Do for Your Agency
UTM parameters (Urchin Tracking Module) are text snippets you add to URLs that track precisely where website visitors come from. When someone clicks a UTM-tagged link, analytics software captures that campaign data, connecting every sale back to its source.
For agencies managing multiple clients, this means you can finally prove which campaigns actually work and which ones drain budgets.
Here’s the transformation in action:
Anatomy of a UTM-Tagged URL
Before: Untracked URL
After: Tracked URL with UTM Parameters
utm_source
utm_medium
paid-social
utm_campaign
winter-sale-2025
Now when someone buys those boots, you know exactly which Facebook campaign drove that sale.
The Five UTM Parameters Every Agency Needs
Think of UTM parameters as a digital filing cabinet for your client traffic. Each parameter captures a different piece of the attribution puzzle.
utm_source – Where Traffic Comes From
This identifies exactly where visitors came from:
utm_source=facebook(Facebook posts or ads)utm_source=google(Google search or ads)utm_source=newsletter(Email campaigns)utm_source=linkedin(LinkedIn posts or ads)
utm_medium – How They Got There
This categorizes the marketing channel. Google Analytics 4 requires specific values for proper channel grouping:
utm_medium=email(Email campaigns)utm_medium=cpc(Paid search ads)utm_medium=social(Organic social posts)utm_medium=paid-social(Social media ads)utm_medium=display(Banner advertisements)
utm_campaign – The Specific Campaign
This names your marketing campaign:
utm_campaign=black-friday-2025utm_campaign=product-launch-q1utm_campaign=customer-retention-email
utm_content – Creative Variations (Optional)
This differentiates between versions of the same campaign:
utm_content=red-cta-buttonutm_content=hero-bannerutm_content=sidebar-ad
utm_term – Keywords or Audiences (Optional)
This tracks specific targeting:
utm_term=running-shoes(Paid search keywords)utm_term=fitness-enthusiasts(Audience segments)
UTM Implementation Guide for Agencies
Here’s how to systematically implement UTM tracking across your agency and client campaigns.
Tool Selection and Setup
Start with Google’s Official Builder Google’s Campaign URL Builder provides the official GA4-compatible tool. Enter your parameters and get instant, properly formatted URLs.
Scale with Enterprise Platforms For agencies running campaigns across multiple clients:
UTM.io offers templates, validation rules, and team collaboration with automated error checking.
Terminus provides enterprise UTM governance with centralized databases and enforced naming conventions.
You can also use our free UTM URL builder below:
UTM Parameter Builder
Create properly formatted tracking URLs in seconds
Base URL Required
Your website URL without any parameters
utm_source Required
utm_medium Required
utm_campaign Required
Use hyphens, lowercase only
utm_content Optional
Differentiate ad variations
utm_term Optional
Keywords or audience segments
Your Tracked URL
Best Practices
Always use lowercase letters
Use hyphens to separate words
No spaces or special characters
Keep names descriptive but concise
Be consistent across campaigns
Never tag internal links
Foundation Setup
Audit Current State
- Review existing campaign links across all clients
- Identify tracking gaps in current campaigns
- Document any existing naming conventions
Create Standards
- Develop UTM naming convention document
- Choose parameter values for each marketing channel
- Set up centralized tracking spreadsheet with approved values
Establish Rules That Prevent Data Disasters
Rule 1: Always Use Lowercase “Facebook,” “facebook,” and “FACEBOOK” create three separate sources in reports. Stick to lowercase: utm_source=facebook.
Rule 2: Pick One Separator Style Choose hyphens (black-friday-sale) or underscores (black_friday_sale) and never mix them.
Rule 3: Ban Spaces and Special Characters Spaces become %20 in URLs. Special characters can break tracking entirely.
Rule 4: Make Names Clear Six months from now, will utm_campaign=promo_v3_final make sense? Use utm_campaign=winter-boots-promotion instead.
Campaign Implementation
Build Templates
- Create UTM templates for each marketing channel
- Establish approval workflows for campaign launches
- Train team members on proper UTM usage
Tag Active Campaigns
- Apply UTM parameters to all running campaigns
- Update existing campaigns with proper tracking
- Set up automated tagging where platforms support it
Test Integration
- Configure hidden form fields for CRM integration
- Test complete attribution flow from click to conversion
- Verify data appears correctly in analytics
Analysis and Optimization
Build Reporting
- Create custom GA4 explorations for campaign analysis
- Build dashboard templates for client reporting
- Establish regular reporting schedules
Analyze Performance
- Calculate baseline metrics (CAC, ROAS, ROI by channel)
- Identify top-performing and underperforming campaigns
- Document insights for campaign optimization
Maintain Quality
- Audit campaign links monthly for consistency
- Review attribution data for optimization opportunities
- Update UTM standards based on new channels
Platform-Specific Implementation
Each platform handles UTM parameters differently.
Facebook and Instagram Campaigns
Facebook’s dynamic parameters automatically populate values:
utm_source={{site_source_name}}&utm_medium=paid-social&utm_campaign={{campaign.name}}&utm_content={{ad.id}}
{{site_source_name}}becomes “facebook” or “instagram”{{campaign.name}}pulls your actual campaign name{{ad.id}}identifies the specific ad
Google Ads Integration
Enable auto-tagging for gclid parameters while adding manual UTMs as backup. Some browsers strip gclid data.
Email Marketing Platforms
Mailchimp automatically creates UTM parameters when you enable Google Analytics integration.
HubSpot provides customizable UTM templates with workflow automation.
ConvertKit and ActiveCampaign offer similar automated tagging.
Strategy tip: Use platform names as sources (utm_source=mailchimp) for channel-level analysis.
LinkedIn Advertising
LinkedIn’s dynamic UTM tracking uses placeholders:
{{CAMPAIGN_NAME}}for campaign identification{{CAMPAIGN_ID}}for unique campaign tracking
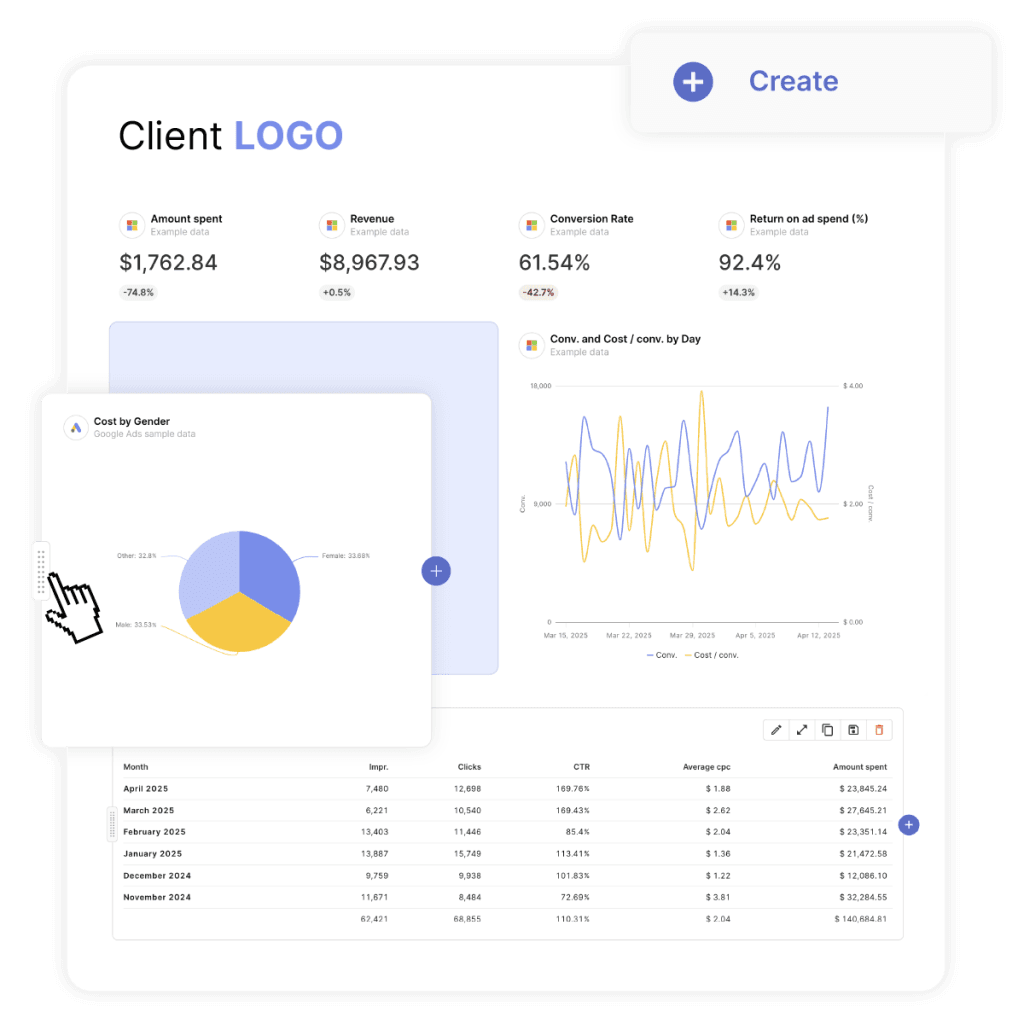
Critical Mistakes That Destroy Attribution Data
Avoid these technical errors and operational pitfalls that permanently corrupt client data.
Technical Errors That Break Tracking
Fatal Error 1 – Internal Link Tagging Never add UTM parameters to internal website links. This starts new sessions and erases the original referrer.
What destroys data:
<a href="/product-page?utm_source=homepage&utm_medium=internal">Shop Now</a>
This turns a Facebook visitor into a “homepage” visitor.
Fatal Error 2 – Case Sensitivity Problems “Facebook,” “facebook,” and “FACEBOOK” appear as three different traffic sources, permanently fragmenting campaign data.
Fatal Error 3 – Source vs Medium Confusion Wrong: utm_source=twitter&utm_medium=twitter Correct: utm_source=twitter&utm_medium=social
Medium describes HOW (channel type), source identifies WHERE (platform).
Fatal Error 4 – Double Parameter Tagging When URLs contain duplicate parameters, Google Analytics uses the last value:
?utm_source=newsletter&utm_medium=email&utm_source=facebook&utm_medium=social
Result: Analytics records this as Facebook social traffic, missing the email attribution.
Operational Pitfalls That Derail UTM Implementation
Pitfall 1 – Perfectionism Paralysis Teams delay implementation while developing complex naming systems. Start with basic conventions and refine over time. Imperfect tracking beats no tracking.
Pitfall 2 – Tool Complexity Overload Complex tools can overwhelm teams. Begin with simple solutions and upgrade as needs grow.
Pitfall 3 – Inconsistent Team Implementation Attribution failures often stem from inconsistent team practices. Invest in comprehensive training and regular refreshers to maintain data quality.
Pitfall 4 – Analysis Procrastination Perfect UTM tags mean nothing without regular analysis. Schedule weekly campaign reviews and monthly deep-dive sessions to extract actionable insights.
Pitfall 5 – Client Education Neglect Clients who don’t understand UTM value may question link aesthetics or complexity. Educate them on attribution benefits before implementation.
Advanced Attribution Strategies for Agency Growth
Move beyond basic tracking with techniques that reveal complete customer journeys.
Multi-Touch Attribution
B2B clients often have long sales cycles with multiple touchpoints. GA4’s attribution models include:
- Data-driven attribution (GA4’s default)
- Last-click attribution for simpler analysis
CRM Integration for Client Reporting
Capture UTM data in your client’s CRM:
<input type="hidden" name="utm_source" value="">
<input type="hidden" name="utm_medium" value="">
<input type="hidden" name="utm_campaign" value="">
<script>
document.querySelector('input[name="utm_source"]').value = getUrlParameter('utm_source');
</script>
This preserves campaign context through form submissions, enabling campaign-to-close attribution.
Cross-Device Journey Tracking
Solutions for tracking users across devices:
- User ID implementation for logged-in users
- Email capture early in the journey
- Consistent UTM tagging across device-specific campaigns
Privacy-Compliant Tracking
UTM parameters collect anonymous behavioral data without personally identifiable information.
GDPR and CCPA Compliance
UTM parameters are privacy-compliant since they track campaign behavior, not personal identity.
Best practices:
- Implement consent management before analytics cookies fire
- Never include PII in UTM parameter values
- Use privacy-friendly analytics when needed
- Document data processing activities
iOS 14.5+ App Tracking Transparency
Apple’s App Tracking Transparency doesn’t affect UTM parameters for web traffic. UTM tracking works regardless of IDFA opt-in status.
Third-Party Cookie Independence
UTM parameters operate independently of cookies, providing first-party attribution data regardless of browser cookie policies.
How to Measure ROI for Client Reporting
Transform UTM data into client-ready insights.
Campaign Performance Metrics from UTM Data
Customer Acquisition Cost
Total Campaign Spend
÷
New Customers
Campaign Example
$5,000 ÷ 100 customers
Return on Ad Spend
Campaign Revenue
÷
Campaign Cost
Campaign Example
$20,000 ÷ $5,000
Campaign ROI (%)
(Revenue – Cost)
÷
Cost × 100
Campaign Example
($20,000 – $5,000) ÷ $5,000 × 100
What These Numbers Mean
$50 CAC
You spend $50 to acquire each new customer from this campaign
4:1 ROAS
For every $1 spent, you generate $4 in revenue
300% ROI
Campaign generated 3x profit on top of the original investment
GA4 Reporting Structure
GA4 structures UTM data across:
- Traffic Acquisition Reports – Most recent campaign that brought users
- User Acquisition Reports – Original campaign that first brought users
Custom Analysis with GA4 Explorations
GA4’s Exploration features enable:
- Funnel Exploration: Conversion paths from UTM source to goal completion
- Path Exploration: How users with specific UTM parameters navigate sites
- Cohort Analysis: Retention rates by acquisition source
Professional Tools for Agencies
Scale UTM operations across multiple clients.
Free UTM Builders
Google’s Campaign URL Builder: Official GA4-compatible tool.
UTMBuilder.net: Clean interface, no registration required.
Enterprise Platforms
UTM.io: Custom validation rules, team collaboration, Chrome extension integration.
Terminus: Enterprise governance with centralized databases and approval workflows.
Link Management
Bitly: URL shortening with UTM management and click analytics.
Rebrandly: Custom branded domains while preserving UTM parameters.
Validation Tools
Google Tag Assistant: Chrome extension for validation.
GA4 Real-Time Reports: Test campaign links before launch.
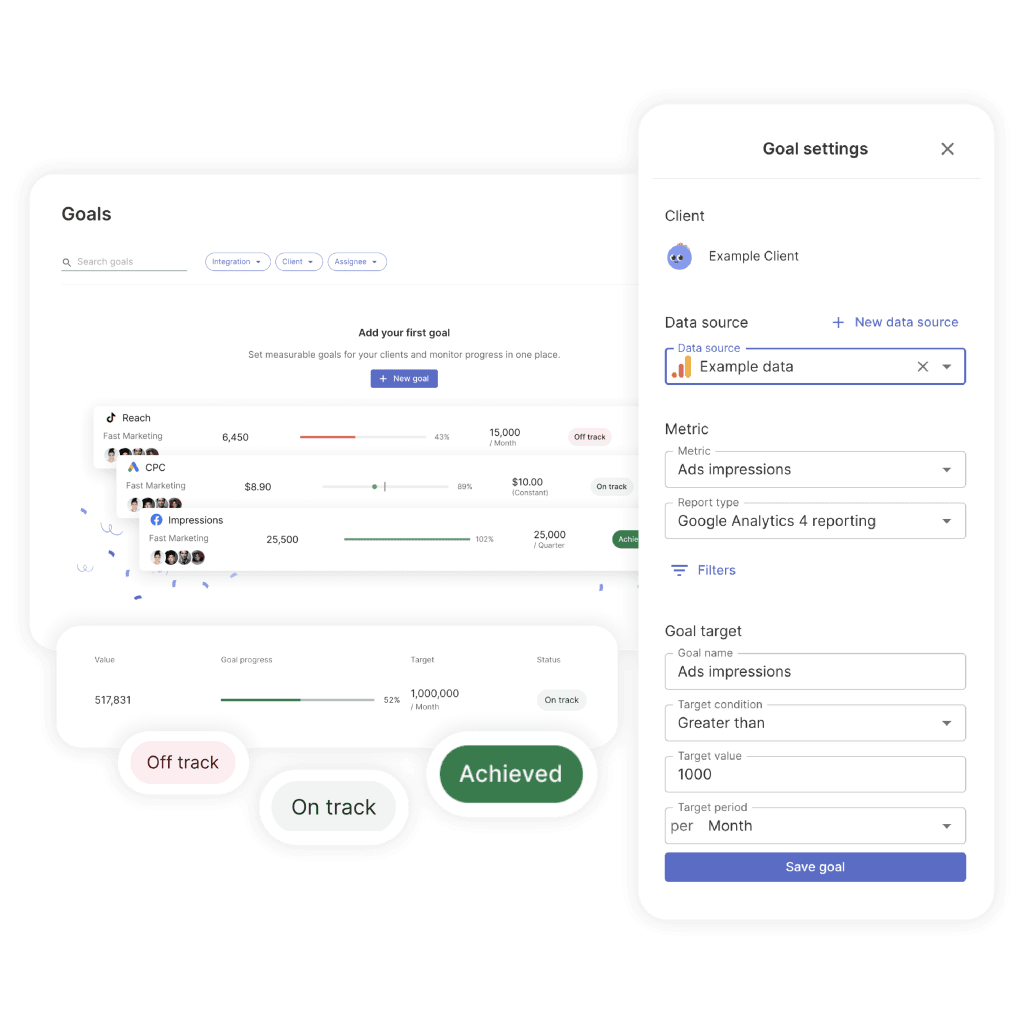
Make UTM Data Actionable for Clients
Convert tracking data into growth decisions.
Campaign Performance Benchmarks
Establish baseline performance metrics for each channel:
- Email marketing: Open rates vary by industry, typically 15-25%
- Paid social: Click-through rates generally range 1-2%
- Paid search: Conversion rates often fall between 2-5%
Attribution Model Selection
Choose attribution models based on client business type:
- E-commerce with short sales cycles: Last-click attribution
- B2B with long sales cycles: Data-driven attribution
- Content-driven businesses: Data-driven attribution
Budget Optimization Framework
Systematically reallocate client marketing spend:
- Calculate true cost per acquisition by channel
- Identify channels delivering lowest CAC
- Test budget shifts from high-CAC to low-CAC channels
- Monitor conversion volume to verify quality maintains
Key Takeaways
Three things separate agencies that prove ROI from those that guess:
Start with naming conventions before you launch anything. Create a simple spreadsheet with approved utm_source and utm_medium values for each platform. Stick to it religiously. Case sensitivity will fragment your data permanently.
Automate where possible, validate everything else. Use Facebook’s dynamic parameters and Google’s auto-tagging, but always add manual UTMs as backup. Test every link in GA4 Real-Time reports before campaigns go live.
Connect UTM data to revenue, not just traffic. Set up hidden form fields to capture campaign data in your client’s CRM. Calculate actual CAC and ROAS by channel. Show clients which campaigns drove real sales, not just clicks.
Most agencies lose attribution data through sloppy implementation, then wonder why clients question their value. UTM parameters work when cookies don’t, platforms change, and privacy regulations tighten. Get this right once, and you’ll have reliable attribution data regardless of what happens next.
The math is simple: Agencies with proper UTM tracking can prove ROI. Agencies without it are selling hope.
UTM Parameters FAQ
Common questions about campaign tracking and attribution
UTM parameters are text snippets added to URLs that track where website visitors come from. They consist of five tags: utm_source (platform), utm_medium (channel type), utm_campaign (campaign name), utm_content (ad variation), and utm_term (keyword). When someone clicks a UTM-tagged link, analytics software captures this data and shows exactly which campaign drove that visit.
UTM stands for Urchin Tracking Module. Urchin was a web analytics company acquired by Google in 2005 that became the foundation for Google Analytics. The UTM parameter naming convention has remained the standard for campaign tracking across all analytics platforms.
UTM parameters tell you which marketing campaigns actually drive results. Without them, you can’t distinguish between a sale from your Facebook ad versus your email newsletter. They transform guesswork into certainty, letting you prove ROI, eliminate wasteful spending, and double down on campaigns that work.
Three UTM parameters are required: utm_source (identifies the traffic source like “facebook”), utm_medium (categorizes the channel like “paid-social”), and utm_campaign (names the campaign like “summer-sale”). The other two—utm_content and utm_term—are optional but useful for A/B testing ads and tracking keywords.
No, UTM parameters don’t negatively affect SEO. Google treats URLs with different UTM parameters as the same page and won’t penalize you for duplicate content. However, use canonical tags if you’re concerned, and never use UTM parameters on internal links as this can disrupt analytics session tracking.
Yes, UTM parameters are visible in the browser address bar. They appear as part of the URL after a question mark, like “?utm_source=facebook&utm_medium=social”. If aesthetics are a concern, use URL shorteners like Bitly or Rebrandly to create cleaner-looking links while preserving tracking data.
Use a UTM builder tool. Google’s Campaign URL Builder is free and official. Enter your website URL, then add your source (facebook), medium (paid-social), and campaign name (summer-sale). The tool generates a tagged URL like: yoursite.com?utm_source=facebook&utm_medium=paid-social&utm_campaign=summer-sale. Copy this URL and use it in your marketing campaigns.
Always use lowercase letters (utm_source=facebook not Facebook), separate words with hyphens (summer-sale not summer_sale), avoid spaces and special characters, and keep names descriptive but concise. Create a naming convention document before launching campaigns because UTM parameters are case-sensitive—”Facebook” and “facebook” will appear as separate sources in reports.
For free tools, use Google’s Campaign URL Builder or UTMBuilder.net. For agencies managing multiple clients, try UTM.io (offers templates and team collaboration) or Terminus (enterprise governance with approval workflows). URL shorteners like Bitly and Rebrandly also include built-in UTM creation and management features.
Create a centralized tracking spreadsheet with columns for campaign name, all UTM values, final URL, launch date, and owner. Document your naming conventions upfront with approved values for each platform. Use tools like UTM.io for team collaboration and automated validation to prevent errors before campaigns launch.
Yes. Always add UTM parameters first, then shorten the complete URL. Services like Bitly and Rebrandly preserve all tracking parameters when redirecting users. This gives you cleaner-looking links for social media while maintaining full attribution tracking—the best of both worlds.
Use Facebook’s dynamic parameters: utm_source={{site_source_name}}&utm_medium=paid-social&utm_campaign={{campaign.name}}&utm_content={{ad.id}}. Facebook automatically populates these values—{{site_source_name}} becomes “facebook” or “instagram”, {{campaign.name}} pulls your campaign name, and {{ad.id}} identifies the specific ad. Add these to your ad’s URL parameters field.
Yes, but also enable Google’s auto-tagging. Auto-tagging adds GCLID parameters automatically, but manual UTM parameters provide backup if account connections break or you switch analytics platforms. Use both for redundancy: utm_source=google&utm_medium=cpc&utm_campaign=your-campaign-name plus Google’s auto-tagging.
Set utm_source to your email platform (mailchimp, constant-contact) or “newsletter”, utm_medium to “email”, and utm_campaign to the specific send (weekly-newsletter-jan or product-launch). Use utm_content to differentiate links within the email (header-cta, footer-link). Most email platforms like Mailchimp offer automatic UTM tagging—just enable it and customize the values.
Yes. Without UTM parameters, organic social traffic shows as direct traffic or gets misattributed. Tag organic posts with utm_source=facebook (or linkedin, twitter), utm_medium=social, and utm_campaign describing the post (product-announcement or blog-promotion). This lets you measure organic social ROI alongside paid campaigns.
LinkedIn offers dynamic UTM tracking with placeholders: {{CAMPAIGN_NAME}} for campaign identification and {{CAMPAIGN_ID}} for unique tracking. For manual tagging, use utm_source=linkedin, utm_medium=paid-social (for ads) or utm_medium=social (for organic posts), and utm_campaign with your campaign name.
In Google Analytics 4, go to Reports > Acquisition > Traffic Acquisition to see utm_source, utm_medium, and utm_campaign data. For more detailed analysis, use the Explore feature to create custom reports filtering by specific UTM parameters. Set up the GA4 tracking code on your website first—UTM parameters won’t appear without it.
Click your UTM-tagged link, then immediately check Google Analytics 4’s Real-Time report (Reports > Real-time). You should see your visit with the correct source, medium, and campaign attribution within seconds. Use Google Tag Assistant Chrome extension for additional validation before launching campaigns.
Yes, using hidden form fields. Add hidden fields named utm_source, utm_medium, and utm_campaign to your lead forms. Use JavaScript to automatically populate these fields from the URL when someone submits the form. This passes campaign data directly into your CRM, connecting leads to their original marketing source.
In Google Analytics, UTM data lasts for the duration of a user’s session (typically 30 minutes of inactivity). However, GA4 tracks both the first campaign that brought a user (User Acquisition) and the most recent campaign (Traffic Acquisition). For longer attribution, capture UTM values in your CRM using hidden form fields.
utm_source identifies WHERE the traffic came from (facebook, google, newsletter), while utm_medium categorizes HOW they got there (email, cpc, social, paid-social). Think of medium as the channel type and source as the specific platform. For example: utm_source=facebook & utm_medium=paid-social tells you it’s a Facebook ad, not an organic post.
Use utm_content when A/B testing different ad variations within the same campaign. For example, if you’re testing two different call-to-action buttons, use utm_content=blue-cta and utm_content=red-cta. This shows which specific ad creative drives more conversions while keeping everything else constant.
Use utm_term to track paid search keywords (utm_term=running-shoes) or audience segments (utm_term=fitness-enthusiasts). While Google Ads auto-tagging captures keyword data automatically, utm_term is useful for other paid search platforms or when manually tagging audience-specific campaigns on social media.
Check these common issues: Google Analytics tracking code missing on the destination page, redirects stripping parameters before reaching the final URL, clicking UTM-tagged links while already on your website (which doesn’t create a new session), or case sensitivity creating data fragmentation. Test using GA4 Real-Time reports immediately after clicking to identify where tracking breaks.
Never. Adding UTM parameters to internal links (links from one page of your website to another) starts a new session in analytics and erases the original traffic source. This makes a Facebook visitor appear as coming from your homepage instead. Only use UTM parameters on external links—those posted on social media, in emails, or on other websites.
You’ll fragment your data permanently. UTM parameters are case-sensitive, so “Facebook”, “facebook”, and “FACEBOOK” appear as three separate sources in analytics. This cannot be fixed retroactively—the historical data remains split forever. Always use lowercase and document your naming conventions to ensure team consistency.
Yes, if not configured correctly. Most redirects (301, 302) should preserve query parameters including UTMs, but some platforms strip them by default. Test your redirect chain by clicking a UTM-tagged link and checking if the parameters remain visible in the final URL. Configure your hosting platform or CDN to preserve query parameters during redirects.
Yes, UTM parameters are privacy-compliant because they track campaign behavior, not personal identity. They don’t collect personally identifiable information. However, implement consent management before analytics cookies fire, never include PII in UTM values, and document your data processing activities to maintain full compliance.
Yes. UTM parameters operate independently of cookies, providing first-party attribution data regardless of browser cookie policies or third-party cookie blocking. This makes them more reliable than cookie-dependent tracking methods, especially as privacy regulations tighten and browsers phase out third-party cookies.
GCLID (Google Click Identifier) is Google’s automatic tracking parameter for Google Ads, while UTM parameters work universally across all platforms. GCLID only functions within Google’s ecosystem and requires linked accounts. UTM parameters are platform-agnostic and readable in any analytics tool. Use both together: enable Google’s auto-tagging while also adding manual UTM parameters as backup.
Connect your UTM data to client reports that prove ROI automatically.
Start Your Free Trial Today- What UTM Parameters Actually Do for Your Agency
- The Five UTM Parameters Every Agency Needs
- UTM Implementation Guide for Agencies
- Platform-Specific Implementation
- Critical Mistakes That Destroy Attribution Data
- Advanced Attribution Strategies for Agency Growth
- Privacy-Compliant Tracking
- How to Measure ROI for Client Reporting
- Professional Tools for Agencies
- Make UTM Data Actionable for Clients
- Key Takeaways
- UTM Parameters FAQ
